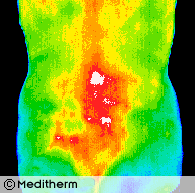
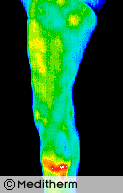
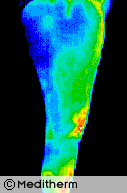
A 32 year old housewife and mother presented with acute back pain with right L2 and L3 sensory and motor nerve root involvement.
Thermography confirmed right L2/L3 root irritation and myelography and CT scan showed a large right L2/L3 prolapse with L4/L5 root involvement.
Thermography shows excellent correlation with CT, MRI and Myelography in radiculopathy.
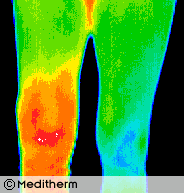
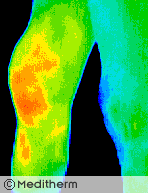
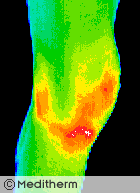
Right knee surgery was followed with a painful effusion in the early post operative period.
Thermography confirmed a significant inflammatory reaction. 30cc of blood-stained fluid was aspirated.
Thermography can quantify all grades of joint synovitis and is able to demonstrate minimal changes due to NSAID’s
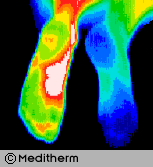
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome right foot, significant increase in sympathetic motor tone right foot 3.7° colder than left foot. A cold stress test was positive, (no sympathetic change).
CRPS developed in the right foot after a fractured calcaneum 18 months previously. Weight bearing was painful. The diagnosis of CRPS was missed initially since nuclear imaging was not typical of CRPS.
Some cases of CRPS are misdiagnosed as psychological or hysterical pain states. Thermography is able to show characteristic changes if utilised.
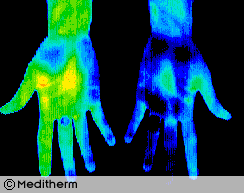
Post-Traumatic Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. A 34 year old female supermarket worker injured her left wrist 3 years previously. There were typical features of CRPS including severe persistent pain and colour and temperature changes in the left wrist and hand.
There was a good initial response to a right cervical sympathectomy but a year later symptoms returned. Treatment with I.V. Guanethidine gave some relief and reduced the temperature differentials significantly from a deltaT of 6.2° pre treatment to 0.8° post treatment.
Thermographic monitoring of sympathetic blockade provides useful objective data to quantify effectiveness of previous blockade and prospective treatments.
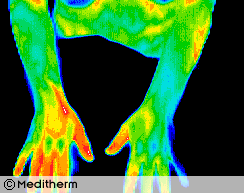
A 28 year old male carpet layer presented with a clinical left carpal tunnel syndrome, The EMG was normal but the left median sensory nerve latency and amplitude suggested minimal dysfunction relative to the right side. Thermography during sympathetic challenge (cold stress test) showed sympathetic nerve dysfunction consistent with an early left carpal tunnel syndrome.
Thermographic sensitivity for detection of early carpal tunnel syndrome is improved by cold stressing both hands. Sympathetic nerve fibres in the symptomatic median nerve are hyperirritable producing a sustained response during cold stress.
